Shipping freight by rail is a key component of the overall shipping process, letting businesses move goods across long distances affordably. While trucks offer versatility and access to more destinations, knowing how and when to use rail services is important for any aspiring shipper.
Key Takeaways
This article explores the fundamentals of rail freight transport, including pricing, advantages, and disadvantages.
I’ll start by reviewing a handful of key terms and definitions that apply to most, if not all, forms of rail shipping.
Now that we have these terms in mind, let’s take a look at how rail companies determine shipping rates.
The price of rail transportation in the United States is usually determined via a system called differential rate shipping. You won’t usually get a final price until some back and forth with a broker or carrier. However, a solid understanding of differential pricing can serve you well when looking for rail carriers.
Differential rates split the carrier’s shipping costs into two categories:
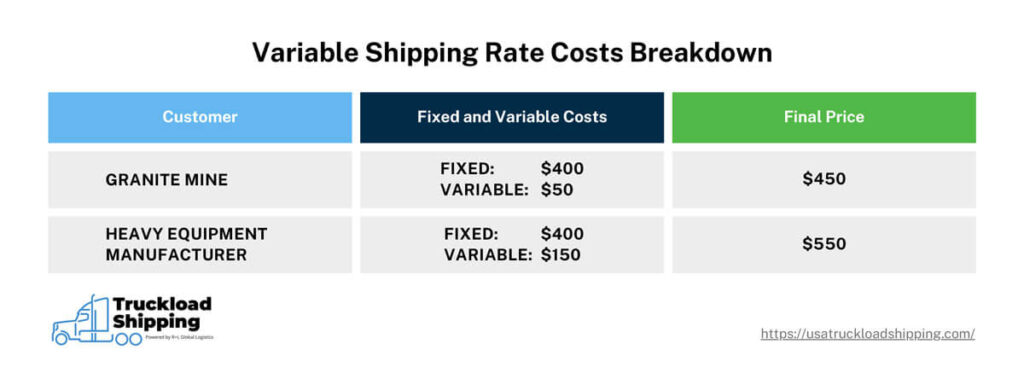
To get an idea of how this works, assume a rail transport company has two shipments to pick up on a trip: one from a granite mine and another from a manufacturer of heavy machinery. While the mine operates like clockwork and has multiple carrier options, the manufacturer often has to meet short-term goals with little notice to serve their customers properly, and their shipping options are limited.
The trip will have fixed costs of $800 and variable costs of $200 for a total carrier cost of $1,000. Each customer pays an equal portion of the fixed costs ($400 a piece), but the rail company charges only 25% of the variable costs to the granite mine ($50) while charging the manufacturer the remaining $150.
Shippers should keep in mind that pricing information between carriers and their customers is usually confidential. Even if you do find out what a customer with comparable needs is paying for carrier service, your rate may be higher or lower depending on the previously mentioned variables.
Another factor to keep in mind is that over long distances, rail shipping costs tend to be lower than comparable truckload (FTL) and less-than-truckload (LTL) shipping. Trains can carry significantly more cargo with fewer resources, which means you could save hundreds of dollars per ton per mile on a similar shipment sent over the road.
Related: Shipping by Rail vs Truck: Everything You Need to Know
Given the variety of goods that travel by rail, carriers have developed a number of specialized train cars to make transport safer and more efficient. Some of these cars include:
In total, 2023 alone saw over $203 billion dollars worth of widely-varied cargo moved across the railways of the United States. To help you determine if rail shipping should be part of your logistics plan, it’s worthwhile to know what goods and products benefit most from this mode of transportation.
While almost any good or commodity can be shipped by rail, some make more sense than others due to shipment volume, size, or the type of cargo in question. Let’s break down
some of the most popular candidates for rail transport.
Even if your shipments don’t fall within these categories, you may find that rail freight transport should be part of your shipping strategy after thoroughly considering its advantages.
I’ve mentioned that rail transport is an effective way to move goods across long distances. Some specific advantages of this shipping method are:
Conversely, shippers should be aware of the inherent limitations of rail transport.
While rail freight transport offers significant cost savings and efficiency for large shipments, it’s rare to be able to use rail exclusively to ship goods. Instead, you’ll need to use intermodal shipping to address every point in the supply chain.
Think about the overall journey of a product from a manufacturer to a distributor and, finally, to the end user. Unless the item was made within proximity to you, it probably spent time on at least two forms of transportation while in transit. This is intermodal shipping: the use of multiple shipping modes to move freight across the supply chain.
If you plan to ship nationally, you’ll need trucks, freight vessels, and even cargo jets at your disposal. Working with a third-party logistics provider will help you determine the fastest, most efficient way to move your shipments across the country.
Rail freight transport is cost-effective, fuel-efficient, and offers a secure shipping solution for bulk cargo and long-distance transportation. Businesses that want to benefit from integrating rail into their logistics strategies can do so easily by partnering with a third-party logistics provider (3PL) such as ourselves.
USA Truckload Shipping’s network of warehouses, carriers, and distribution centers is set up to store and ship freight of all sizes and transit requirements. We can help you meet customer expectations while maintaining profitability in the complex world of logistics.
Our services include:
Call us today at (866) 353-7178 or submit a request for proposal online. We have the experience and resources you need to keep your shipping goals on track.
R+L Global Logistics
315 NE 14th St., Ocala, FL 34470